Comprehensive Guide to Quality Assurance (QA) and Testing
Quality Assurance (QA) is the foundation that keeps software reliable, efficient, and valuable for both businesses and their customers. Instead of focusing only on fixing errors after they appear, QA emphasizes building strong processes that reduce risks from the very beginning. This means looking at how teams work, how software is developed, and how potential problems can be avoided before they ever reach the user.
For any business that depends on digital tools or applications, QA becomes more than a technical task—it’s a business strategy. It helps protect your investment, supports customer satisfaction, and safeguards your reputation in a competitive market.
In this guide, we will break down what QA truly involves, highlight the benefits it brings to organizations, explore the most common tools and techniques, and share proven practices that can strengthen the way your business approaches software development.
Benefits of Quality Assurance and Testing
Quality Assurance (QA) is more than just a technical safeguard—it is a business enabler. By integrating QA into your development process, your company can secure long-term value, protect customer trust, and maintain operational efficiency. Let’s look at the key benefits in detail.
1. Enhances Product Quality
At its core, QA ensures your product consistently meets customer expectations. It is not only about removing defects but also about building confidence that the software will perform reliably in different scenarios. A well-tested product earns user trust, strengthens loyalty, and reduces the chances of costly reputational damage.
2. Reduces Development Costs
Addressing issues early saves both money and time. Without QA, small coding errors can evolve into major failures once the product reaches the market. Fixing them post-launch often demands significant resources. QA lowers these risks by catching issues at the earliest stage, making development more cost-effective.
3. Boosts Team Efficiency
A structured QA process allows developers to focus on creating features while testers handle stability and quality checks. This clear division of roles reduces bottlenecks, shortens project timelines, and ensures smoother collaboration across teams.
4. Supports Regulatory Compliance
For businesses in highly regulated sectors such as finance or healthcare, QA is essential for compliance. It ensures products adhere to strict standards, helping organizations avoid legal challenges, fines, and reputational harm.
5. Improves User Experience
A seamless user experience is central to customer retention. QA identifies performance bottlenecks, usability issues, and potential risks before customers encounter them. This proactive approach creates smoother interactions and enhances satisfaction.
In essence, QA is not just about testing—it’s about protecting your business, optimizing processes, and ensuring long-term success.
Common Quality Assurance Tools
Selecting the right Quality Assurance (QA) tools is not just a technical choice—it directly impacts the efficiency, accuracy, and reliability of your software development process. Each tool plays a specific role in helping your business deliver high-quality products while minimizing risks.
- Selenium: As one of the most trusted automation frameworks, Selenium simplifies the testing of web applications across different browsers. For businesses, this ensures consistency in user experience regardless of the platform customers choose.
- JIRA: More than just a project management tool, JIRA is central to tracking issues and managing testing workflows. By offering visibility into progress and challenges, it helps teams stay aligned and accountable.
- TestRail: TestRail brings structure to test planning and execution. Its integration with other tools, such as JIRA and Selenium, makes it easier for teams to collaborate, ensuring no step in the testing process is overlooked.
- Postman: For businesses relying on APIs, Postman is invaluable. It validates how different systems communicate, helping to guarantee smooth functionality and reduce disruptions for end-users.
- Appium: With the growth of mobile applications, Appium addresses the need for testing across both iOS and Android. It supports different app types, ensuring mobile users enjoy reliable and seamless performance.
- Apache JMeter: Performance under pressure is critical. JMeter simulates heavy usage, allowing businesses to understand how their system will behave under stress and prepare for high-demand scenarios.
Together, these tools strengthen your QA process, enabling your business to deliver trustworthy digital products.
Common QA Techniques
Quality Assurance (QA) combines multiple techniques to ensure software works as intended, delivers value to customers, and protects business interests. Each technique addresses a different layer of quality, and together they create a comprehensive safety net for your digital products.
1. Manual Testing
Manual testing relies on human effort to explore the application step by step. Unlike automated checks, it allows testers to think creatively and uncover issues that machines may overlook, such as confusing layouts or unclear instructions. For businesses, this type of testing is valuable when evaluating user experience, as it mirrors how real customers interact with the product. While slower than automation, it provides insights that cannot be replaced by tools alone.
2. Automated Testing
Automation reduces repetitive manual work by using specialized tools to run tests quickly and consistently. It is especially effective for regression testing, ensuring that existing features still work after updates, and for performance testing under different loads. Businesses benefit from faster release cycles, reduced human error, and greater confidence that software changes will not disrupt core functions.
3. Unit Testing
Unit testing examines individual components of software in isolation, much like checking each brick before constructing a building. This technique prevents small errors from escalating into larger failures. For businesses, strong unit testing reduces rework, accelerates debugging, and increases stability from the earliest development stages.
4. Integration Testing
Software rarely operates as a single piece; it integrates multiple systems and services. Integration testing verifies that these components work together seamlessly. For example, a payment system must properly connect with a shopping cart. When done correctly, it reduces breakdowns that can frustrate customers and damage trust.
5. Functional Testing
This technique ensures the application fulfills its intended purpose. Testers validate core features, business logic, and user requirements, confirming that the software delivers what was promised. From a business perspective, functional testing ensures alignment with customer expectations and prevents costly mismatches between product design and actual performance.
6. Performance Testing
A system may function correctly in small-scale use but fail under heavy demand. Performance testing examines speed, scalability, and reliability during peak conditions. By identifying bottlenecks in advance, businesses can prepare for high-traffic scenarios—such as product launches or seasonal spikes—without risking downtime or lost revenue.
8. Security Testing
In a world where data breaches make headlines, security testing is non-negotiable. It uncovers weaknesses like unauthorized access points or insecure data handling. Beyond protecting sensitive customer information, it shields businesses from legal consequences, financial loss, and reputational harm. Strong security testing builds confidence that your product is both safe and trustworthy.
When these techniques are applied together, QA becomes more than testing—it becomes a strategic layer of protection and growth for your business.
Best Practices for Quality Assurance and Testing with FIX Partner
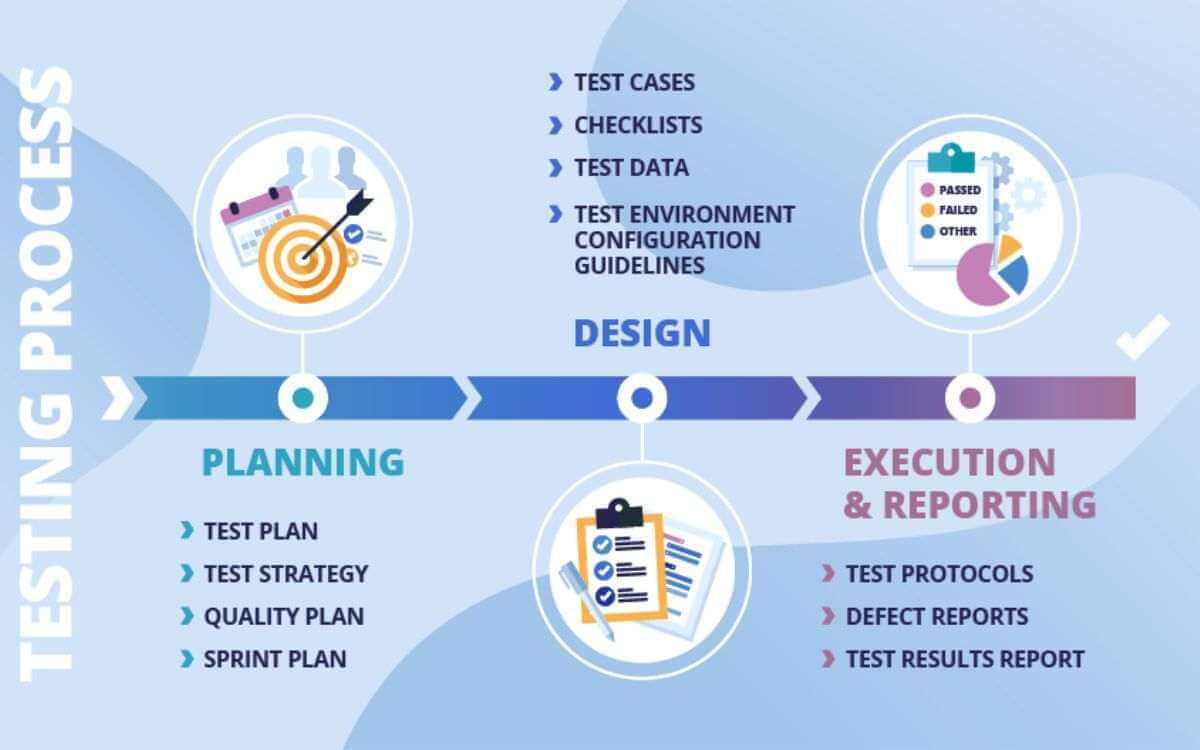
For any business investing in digital products, Quality Assurance (QA) is not just a technical checkpoint—it is a safeguard for your reputation, efficiency, and customer trust. At FIX Partner, we believe QA should be viewed as a business strategy that enables long-term growth. Below are key best practices we recommend to maximize the value of your QA efforts.
1. Start Early in the Development Cycle
Embedding QA from the very beginning prevents small mistakes from turning into expensive failures. At FIX Partner, we integrate testing within Agile workflows, ensuring that potential risks are addressed during design and development rather than after launch. This saves time and money while creating a more reliable product.
2. Create a Detailed Test Plan
A strong test plan is like a roadmap. It defines objectives, scope, resources, and schedules, giving all teams a shared vision. FIX Partner emphasizes structured planning to eliminate confusion, align priorities, and ensure no critical areas are overlooked.
3. Use a Mix of Manual and Automated Testing
Both methods bring unique value; automated testing is fast, consistent, and ideal for repetitive tasks, while manual testing captures human-driven insights into usability and customer experience. FIX Partner blends both approaches to balance speed with depth.
4. Conduct Regular Code Reviews
Code reviews paired with QA uncover issues earlier in the process. This practice not only improves technical quality but also reduces downstream bugs. Our approach ensures cleaner code and smoother development cycles.
5. Leverage Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
Integrating QA into CI/CD pipelines delivers rapid feedback with every update. FIX Partner uses leading tools to automate this process, giving businesses the confidence to release updates frequently without compromising quality.
6. Prioritize Test Cases Based on Risk
Not all features carry the same weight. We help businesses focus testing efforts on high-risk areas—such as payment systems or data security—where failure could have a significant financial or reputational impact.
7. Track Metrics and KPIs
Data-driven QA ensures continuous improvement. FIX Partner tracks key indicators like defect density and test coverage, helping businesses refine strategies and achieve higher efficiency over time.
8. Foster Collaboration Between Teams
Quality cannot exist in silos. We encourage close collaboration between QA, development, and product teams, streamlining communication and resolving issues faster. This teamwork ensures alignment with both technical goals and business objectives.
At FIX Partner, these practices are more than recommendations—they are part of our proven approach to delivering digital solutions that your businesses can trust.
Conclusion
Quality Assurance (QA) is more than just a phase in the software development lifecycle; it is an ongoing commitment to excellence. By leveraging the right tools and techniques, businesses can ensure high-quality software delivery, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
With the dynamic nature of technology and user expectations, staying proactive in your QA processes is essential. Make QA an integral part of your development culture, and you’ll reap the long-term benefits of reliable, user-friendly software.
By following best practices and utilizing effective tools, your organization can maintain its competitive edge and deliver exceptional customer value.
Let’s get in touch with us for a free consultation.




